动态深度网络愈发受到业内关注,16年年末和17年年初,先后有dynet、pytorch和TensorFlow Flod三个动态深度框架发布。笔者从16年10月份开始关注dynet,逐步成为该项目的contributor,对这个深度框架整体设计和细节实现都较为了解。dynet虽然代码量较少,但是具备一个现代深度学习框架应有的诸多特定:动态结构、计算流图等。本篇即在笔者的源码阅读心得基础上加以整理归纳,介绍dynet的整体架构和设计思路。后续将会有系列文章介绍dynet的具体实现,以便读者深度了解深度学习框架的设计理念和实现细节。
文章结构
整体介绍
动态深度网络dynet,代码简洁,动态计算流图构建速度也较快。
项目介绍
dynet是一个由CMU clab发起并主导开发的动态深度网络框架,专门针对自然语言处理上的深度学习做了优化和改进。dynet目前支持CPU和GPU两种计算模式,计划加入多GPU支持、模型并行,矩阵计算基于eigen,CPU上计算加速基于cblas。
项目架构
dynet将一个深度网络结构解构为如下几个重要模块:Tensor、Node、Expression、Model、ComputationGraph, SimpleEigen Trainer。每个模块具体含义和实现方式将会在下文做详细介绍。
模块介绍
Tensor
在dynet中,训练过程,所有的数据,都被表示为Tensor,这些数据包括:输入数据、输出数据、网络参数等。Tensor可以说是组成dynet神经网络的基础。Tensor实现在tensor.h和tensor.cc两个文件中。具体实现方法依赖于eigen第三方矩阵计算工具。Tensor有如下成员变量:
Dim d; //shape of tensor
float* v; // pointer to memory
std::<Tensor> bs;
Device* device;
DeviceMempool mem_pool;
dynet中的tensor实际是依赖于eigen实现的,dynet中的tensor只是对eigen::tensor的一次封装,这次封装为eigen::tensor进一步明确了维度、所在device、内存地址等信息。
Node
在dynet网络结构中,Node是网络的实际构建单位。Node既可以是由tensor组成的,也可以是由函数组成的,也就是说,有些node是tensor node,而有些node则是function node,在function node上要做一些计算,function node的输出又是一个tensor。但是有一点需要注意的是,实际上在组建深度网络的时候,我们并不会直接使用到node,取而代之的是建立在node之上的Expression类。通过Expression构件深度网络,简洁方便,而且符合人的书写方式,但是底层的以node组成网络的形式,又方便人类理解计算流图的结构。一个具体的计算流图如下所示:
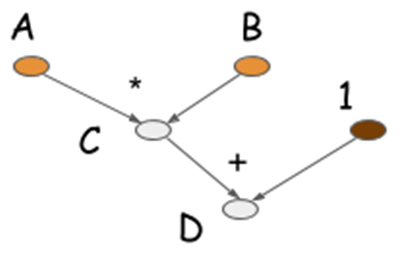 计算流图
计算流图
在dynet中,所有的参数型node都会被其所属的Model持有。Node基类的主要成员函数和成员变量有:
Dim dim_forward(); //计算输入数据的维度是否能够计算,并计算输出数据的维度
void forward_impl(); //前向传播的具体实现
void backward_impl(); // 后向传播的具体实现
void forward(); //前向传播对外调用接口,用于判断当前Node是否支持多批量计算
void backward();
unsigned artiy(); //此node的参数个数
vector<VariableIndex> args; //参数向量
Dim dim; //输出结果维度
Device* device; //Node计算所在的device CPU or GPU
Expression
Expression既是表达式的抽象表示,也是一些常用函数的抽象表示。Expression的基础是node,expression的管理者是ComputationGraph。在dynet中,深度网络由Expression组成,所有的参数在高层语义中都是Expression,只不过依赖于下层的node来做具体实现。下面以一个简单的例子,来看看dynet中,如何使用Expression,组成一个xor的深度网络:
// 创建一个新的网络,参数的持有者是model,所有参数都会保存在model中
const unsigned HIDDEN_SIZE = 8;
p_W = m.add_parameters({HIDDEN_SIZE, 2}); //返回的类型是parameter
p_b = m.add_parameters({HIDDEN_SIZE});
p_V = m.add_parameters({1, HIDDEN_SIZE});
p_a = m.add_parameters({1});
//深度网络参数表达式
Expression W = parameter(cg, p_W);
Expression b = parameter(cg, p_b);
Expression V = parameter(cg, p_V);
Expression a = parameter(cg, p_a);
//组建深度网络
vector<dynet::real> x_values(2); // set x_values to change the inputs to the network
Expression x = input(cg, {2}, &x_values);
dynet::real y_value; // set y_value to change the target output
Expression y = input(cg, &y_value);
Expression h = tanh(W*x + b);
Expression y_pred = V*h + a;
Expression loss_expr = squared_distance(y_pred, y);
上述代码阐明了在dynet中创建网络需要的若干主要步骤:
- 向模型参加所有参数
- 为参数创建表达式实例
- 使用表达式构建深度网络(更直观的说,构建最终的目标函数)
前面交代过Node才是构建深度网络结构的基本单位,但是在上述代码中并未出现过任何Node类的实例,那么dynet是怎么从高层的Expression过渡到底层的Node呢。下面以Parameter w加入到深度网络的过程为例,大致介绍下其中的流程:
-
将paramter转化为Expression (in xor.cc)
Expression w = parameter(ctg, p_W); -
返回Expressin 实例化对象(in expr.cc)
return Expression(&g, g.add_parameter(p)) -
向网络中添加Node(in dynet.cc:add_parameter)
VariableIndex ComputationGraph::add_parameters(Parameter p) { VariableIndex new_node_index(nodes.size()); ParameterNode* new_node = new ParameterNode(p); // 创建新的Node nodes.push_back(new_node); // 将新Node添加到nodes向量中 parameter_nodes.push_back(new_node_index); // w是参数,所以向parameter_nodes中也添加一次 set_dim_for_new_node(new_node_index); return new_node_index; }
ComputationGraph
ComputationGrahph是整个系统最为重要的一个类,它代表着一个深度网络,抽象表示了一个计算流图。用户可以向计算流图中添加输入数据、待优化参数、以及functoin,以及前向计算和后向计算。主要类成员如下所示,
// INPUTS
// the computational network will pull inputs in from the user's data
// structures and make them available to the computation
VariableIndex add_input(real s); // add scalar
...
// PARAMETERS
// parameters are things that are optimized. in contrast to a system like
// Torch where computational modules may have their own parameters, in DYNET
// parameters are just parameters
VariableIndex add_parameters(Parameter p);
VariableIndex add_const_parameters(Parameter p);
...
// COMPUTATIONS
template <class Function> inline VariableIndex add_function(const std::initializer_list<VariableIndex>& arguments);
// forward and backward
const Tensor& forward(const expr::Expression& last);
const Tensor& forward(VariableIndex i);
// run forward pass from the last computed node to given one.
// useful if you want to add nodes and evaluate just the new parts.
const Tensor& incremental_forward(const expr::Expression& last);
const Tensor& incremental_forward(VariableIndex i);
// get forward value for node at index i. used cached values if available,
// performs forward evaluation if note available (may compute more than strictly
// what is needed).
const Tensor& get_value(VariableIndex i);
const Tensor& get_value(const expr::Expression& e);
// clears forward caches (for get_value etc).
void invalidate();
// computes backward gradients from the front-most evaluated node.
void backward(const expr::Expression& last);
// computes backward gradients from node i (assuming it already been evaluated).
void backward(VariableIndex i);
ExecutionEngine* ee; // handles the execution
计算流图虽然包含了整个网络结构,但是实际上的前向计算和后向计算,并不是ComputattionGraph独立完成的,而是借助于一个成员变量 ee(ExecutionEngine)实现的,主要的前向计算、后向计算等等都是由ee执行的。因为在前后向计算中,会用到网络结构,所以ee中包含了对应的ComnputationGraph cg。
ExcutionEngine
Excution类似于TensorFlow中的session,是用于规划和驱动计算流图中的数据流动(PS: engine的作用在于驱动数据流,而不是)。
Model
在dynet中,model是一个较为独立单纯的类,它不会参与实际网络的构建,也不会包括深度网络自身的参数,它只是一个简单的参数存储类,这样的实现方式,有效地将参数和网络结构隔绝。Model的主要成员如下:
std::vector<ParameterStorageBase*> all_params;
std::vector<ParameterStorage*> params;
std::vector<LookupParameterStorage*> lookup_params;
// these are a subset of the parameters that are used when model is updated.
// kept as indices into params and lookup_params.
std::vector<unsigned> updated_params;
std::vector<unsigned> updated_lookup_params;
L2WeightDecay weight_decay;
Trainer
类似于caffe中的Solver,这个类主要包含了诸多的训练中参数,主要作用是更新参数,